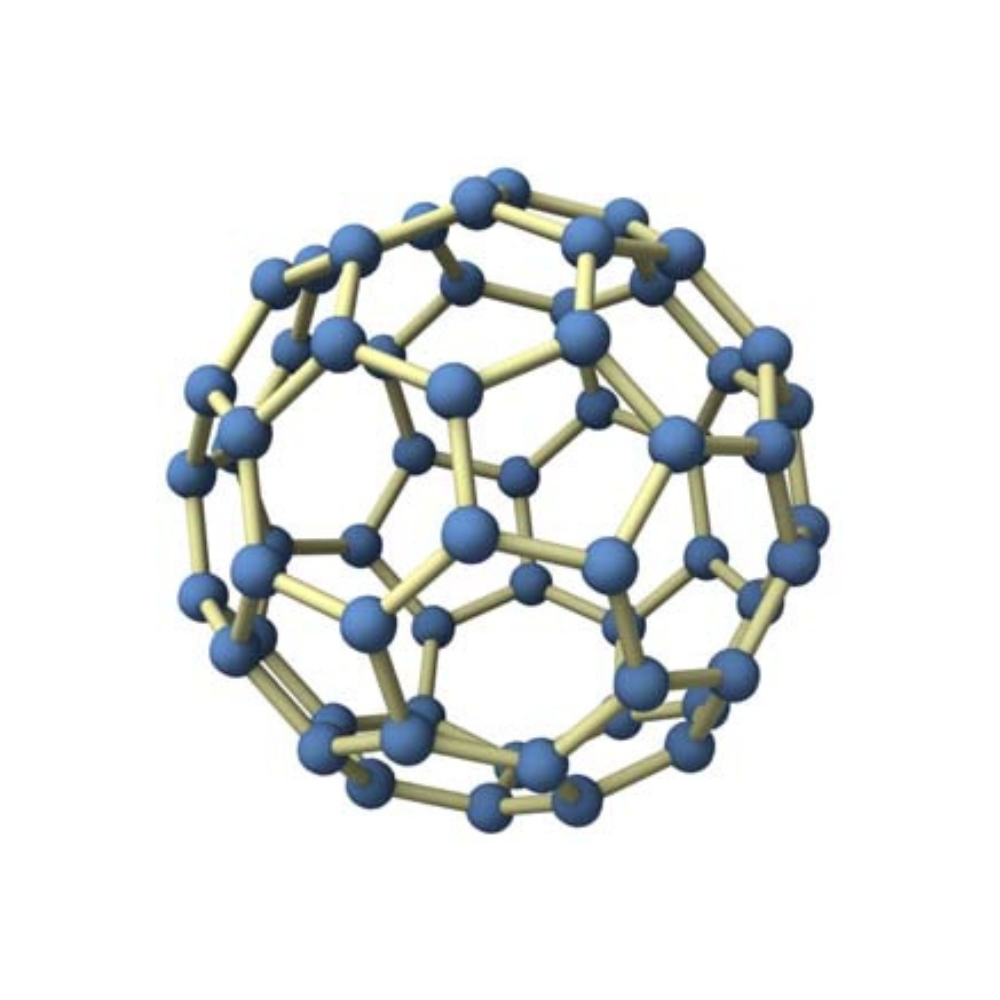
Carbon 60, also known as C60 or fullerene, is a fascinating molecule with an array ofpotential health benefits.
But who discovered this unique molecule?
In 1985, researchers at Rice University in Houston, Texas, discovered C60 while studying the byproducts of laser vaporization of graphite. The researchers were examining the contents of the resulting soot when they discovered a previously unknown molecule with a soccer ball-like structure. This molecule was later identified as C60.
The researchers who discovered C60 were named Richard Smalley, Robert Curl, and Harold Kroto. For their discovery, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1996.
Since its discovery, C60 has been the subject of much research, and its potential applications in a variety of fields have been explored.
In the field of medicine, C60 has been shown to have antioxidant properties and to potentially have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective effects. It’s also been studied for potential use in drug delivery and imaging.
In addition to its potential health benefits, C60 has also been studied for use in materials science, electronics, and energy storage. Its unique structure and properties make it a fascinating molecule with many potential applications.
Why Is The Discovery Of C60 So Important?
The reason the discovery of C60 is so important is because it opened up new fields of research in materials science, nanotechnology, and chemistry. Because of its distinct structure – it has many potential applications in these fields, and potentially many more that we have yet to discover. The molecule also has the potential to be used in drug delivery, as a catalyst, in electronics, and even in energy storage.
The more popular reason is that it has potential health benefits due to its powerful antioxidant properties. Studies have shown that C60 may have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective effects. It has also been shown to improve longevity in animal studies. These discoveries have led to increased interest in C60 as a health supplement.
Finally, the discovery of C60 was a major scientific achievement that led to the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1996 to the researchers who discovered it. This recognition helped to solidify the importance of the discovery and brought it to the attention of the wider scientific community.
Are there any discoveries that are similar to C60?
Yes, there are several other carbon-based structures that are similar to C60 in terms of their unique properties and potential applications. Here are a few examples:
-
Carbon Nanotubes: These are long, cylindrical structures made of carbon atoms. Like C60, they have unique electrical and mechanical properties that make them useful in a variety of applications, including in electronics, energy storage, and as a reinforcing agent in materials.
-
Graphene: Graphene is a two-dimensional carbon structure that is incredibly strong, lightweight, and flexible. It has potential applications in electronics, energy storage, and even as a water filtration material.
-
Carbon Dots: These are tiny particles made of carbon atoms that have unique fluorescent properties. They are being studied for use in imaging and sensing applications.
-
Carbon Quantum Dots: These are similar to carbon dots, but have slightly different properties that make them useful in different applications. They are being studied for use in areas such as bioimaging, sensing, and energy conversion.
-
Carbon Nanobuds: These are structures that combine carbon nanotubes and fullerene molecules (like C60). They have potential applications in areas such as electronics, energy storage, and as a reinforcing agent in materials.
Overall, there are many carbon-based structures that are similar to C60 in terms of their unique properties and potential applications. As research continues in these areas, it is likely that more and more applications for these structures will be discovered.