by Len Heflich | Nov 15, 2019
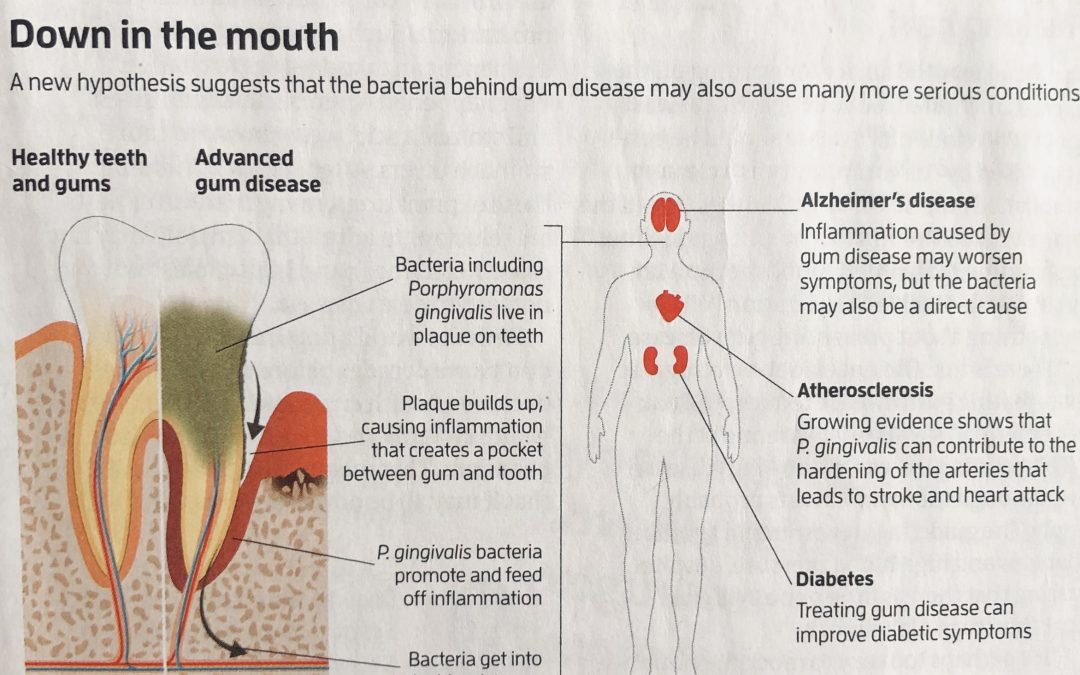
Debora MacKenzie, New Scientist, 10 August 2019, pages 42-46 FOR decades, health experts have been lecturing us about our bad habits, blaming them for the surge in “lifestyle diseases”. These often come on as we age and include heart disease, Alzheimer’s, type 2...

by Len Heflich | Nov 8, 2018
Inflammation is the main reason or accompanying phenomenon almost of all gut disorders, and its elimination is required tor successful therapy. A significant role at all the stages of inflammation and carcinogenesis is attributed to reactive oxygen species...
by Len Heflich | Nov 8, 2018
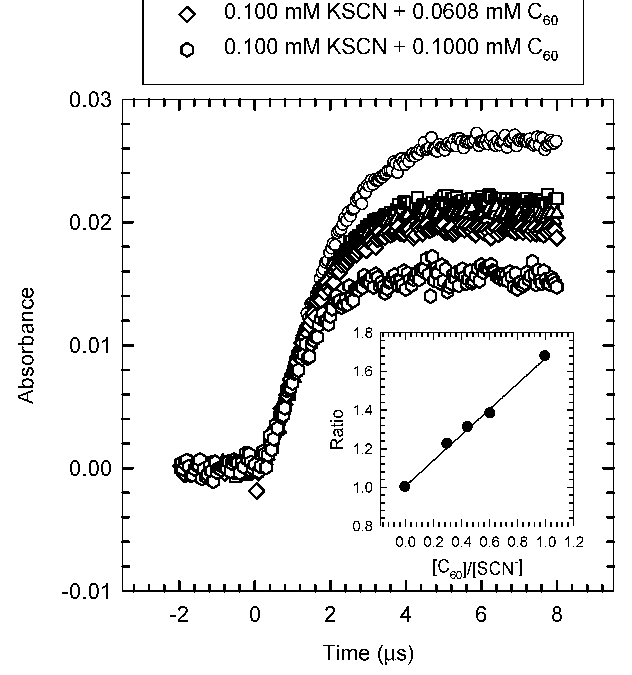
Quantum mechanical calculations of binding energy of the C60−OH adduct as a function of C60 clustering degree indicate, despite an initial fast reaction, a slower overall conversion due to thermodynamic instability of C60−OH intermediates. The results imply that...
by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
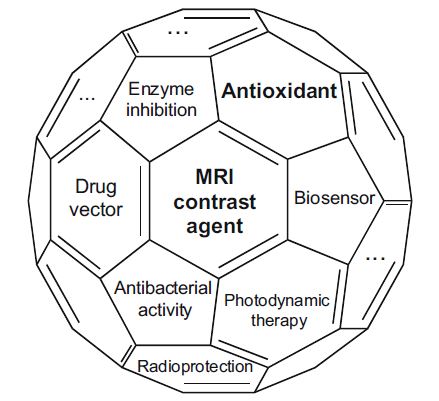
The emerging field of nanotechnology is affirming its increasing importance day by day. In this context fullerenes and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) play an important role. These new allotropic forms of carbon have been discovered in the last two decades, and, since then,...
![The prolongation of the lifespan of rats by repeated oral administration of [60] fullerene](https://www.bioactivec60.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/extended-life-span-of-rats-with-exposure-to-C60.jpg)
by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
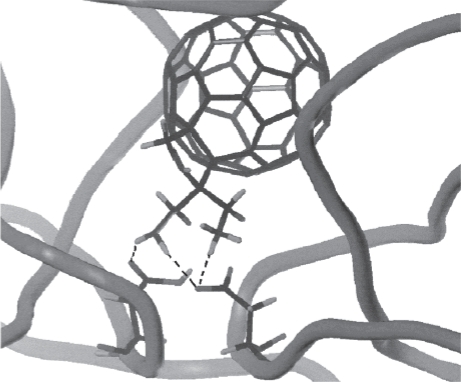
Countless studies showed that [60]fullerene (C60) and derivatives could have many potential biomedical applications. However, while several independent research groups showed that C60 has no acute or subacute toxicity in various experimental models, more than 25 years...
by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
Fullerenes, especially the most studied and well-known fullerene C60, have shown potential medicinal applications due to their unique physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity. Here are some examples of their medicinal applications: Antioxidant: Fullerenes,...
by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
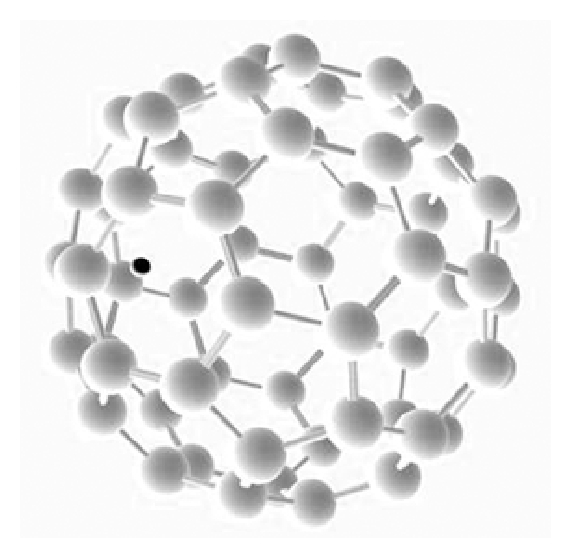
Fullerene C60 is a spherical molecule composed of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a pattern similar to a soccer ball. It has been found to exhibit antioxidant properties due to its ability to scavenge free radicals and prevent oxidative damage. The following are some...

by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
Free radicals are highly reactive and unstable molecules that contain one or more unpaired electrons. Because of their unstable nature, they seek to bond with other molecules, in a process called oxidation, which can cause damage to cells, proteins, and DNA. Free...
by Len Heflich | Oct 22, 2018
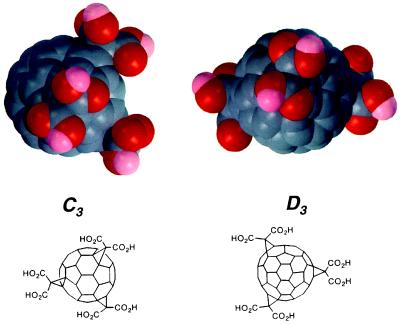
Two regioisomers with C3 or D3 symmetry of water-soluble carboxylic acid C60 derivatives, containing three malonic acid groups per molecule, were synthesized and found to be equipotent free radical scavengers in solution as assessed by EPR analysis. Read full...





![The prolongation of the lifespan of rats by repeated oral administration of [60] fullerene](https://www.bioactivec60.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/extended-life-span-of-rats-with-exposure-to-C60.jpg)




